greenchemistry
Green Chemistry focuses on :
• Reduction, recycling and/or eliminating toxic substances
• Finding creative, alternative routes to minimize impact on
the environment
• More eco-friendly green alternative toconventional
chemistry practices
• Provides sustainable development, sustainable business and
sustainable living practices
Twelve Principles of Green Chemistry
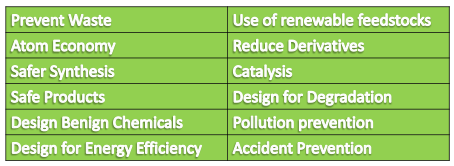
- Prevent Waste :
- Synthesis only targeted product with minimum or no by products/waste
- If waste is produced , it involves cost and time to treat and safely dispose it, as a result production cost increases
- Atom Economy: Synthetic methods should be
- designed to maximize the incorporation of all materials used into the final product
- The chemical processes should have maximum product yield
- Atom economy can be calculated using the relation
- % Atom Economy = (FW of atoms utilized/FW of all reactants) X 100
Atom Economy in a Substitution Reaction - moderate
Atom Economy in Elimination Reactions - low
Atom Economy in Addition Reactions -100%
Atom Economy in Rearrangement Reactions -100%
For a green synthesis atom economy must be maximum (100%)
- Safer Synthesis:
- The synthetic processes should be
- designed so as to minimize or prevent the production of hazardous substances
- Necessary safety precautions have to be taken while processing to protect human health and environment
- eg: Polyurethane is manufactured conventionally using and alcohol. However, isocyanate is produced using phosgene, a toxic gas
- The alternative method by green synthesis of polyurethane eliminates the use of phosgene and uses CO2
- Safe Products : Chemical products should be designed
- to preserve efficacy of function while reducing toxicity
- Products should not have any side effects on the people using it and on the environment
- It is envisaged to produce the chemical products specially those being used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, etc.
- Design Benign Chemicals :
- Use safer solvents and reaction conditions
- Avoid using solvents, separation agents, or other auxiliary chemicals
- If these chemicals are necessary, use innocuous chemicals
- Chemical syntheses are assisted by solvent medium:
- recommended to use alternative solvents , greener in nature such as aqueous medium, liquid carbon-dioxide, ionic liquids(N-alkyl pyridinium cation with BF4-), or solvent free systems
- Avoid harmful solvents like chloroform, pyridine which are known to cause health hazard, are carcinogenic to human beings and animals or cause severe damage to environment
- Design for Energy efficiency :
Chemical processes are to be designed in such a way that they are less energy intensive
- reactions occurring at mild conditions
- require less time to complete
For this purpose it is worthwhile to utilize
- Bio-catalyst, homogeneous and heterogeneous catalyst which reduces the energy of activation
- Modern techniques such as solvent free synthesis, supercritical fluid systems, microwave irradiation, and ultrasound
- Use of renewable feedstock :
- Raw material or feedstock used as starting material should be renewable rather than depleting wherever technically and economically possible
- Use of renewable feedstock such as biomass and agricultural wastes are strongly recommended rather than using non-renewable resources such as coal, petroleum-based raw materials, etc.
- Reduce Derivatives:
- Avoid unnecessary derivatization
- temporary modification should be avoided whenever possible as they generate waste
- the atom efficiency is reduced as the protective group is not incorporated in the final product e.g: blocking group, protection/ deprotection
- Catalysis:
- Use catalytic reactions, as catalysts
- Speed up the reaction can be recycled and are highly selective
- less energy consumption during reaction
- obtaining high yield of product of high purity
Unlike stiochiometric reactions which are energy
intensive require excessive reagents
- Design for Degradation :
- Design chemicals and products to degrade after use to innocuous substances after use so that they do not accumulate in the environment
- Especially applicable to:
- insecticides
- pesticides
- polymers which tend to persist in the environment and are known to cause bioaccumulations
- Pollution Prevention :
- Real-time analysis (quality control)
- Continuously monitor and control the formation of hazardous substances
- Any unreacted reactant can be recycled in order to minimize the use of chemicals
- Accident Prevention :
- Minimize the potential for accidents
- Chemicals chosen for processes should be such which minimise accidents in the form of fires, explosions, and toxic releases to the environment
- Manufacturing plants should be well equipped with safety mechanisms
- The Bhopal gas tragedy is one of the worst industrial disasters
Green chemistry is a set of principles which emphasises on
- environmentally benign chemical synthesis with a view to devise pathways for the prevention of pollution.
- bringing a paradigm shift in chemical processing to achieve sustainable development.